- NdFeB magnets, or neo-magnets, are the strongest permanent magnets available
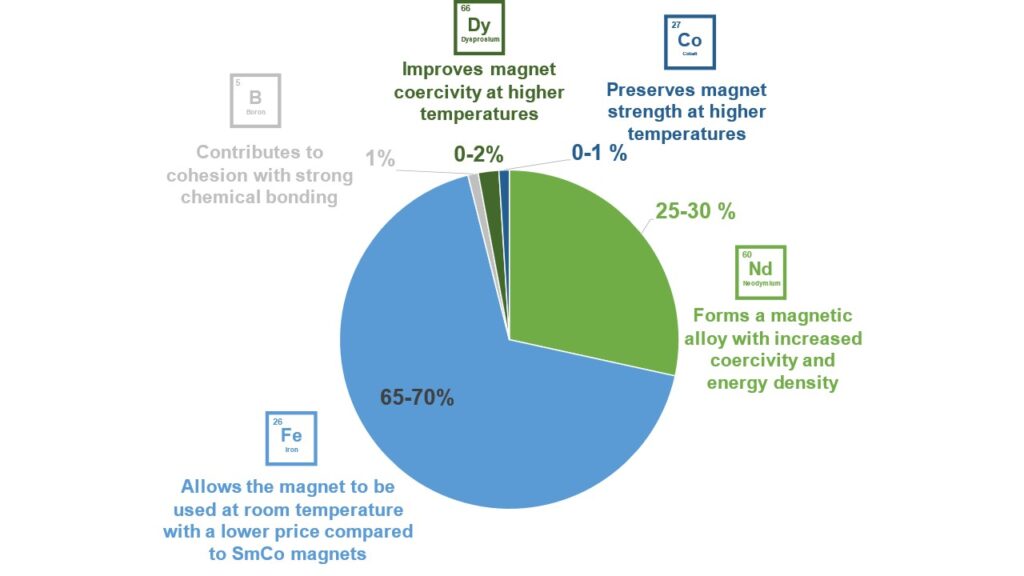
- They are made of a Nd2Fe14B alloy whose crystalline structure promotes a higher coercivity (i.e. resistance to demagnetization) than traditional magnets
- They were developed in the 1980s independently by US General Motors and Sumitomo Corporation (Japan) to alleviate cobalt dependency of rare-earth magnet production
- Cobalt is sometimes added in small quantities to increase the magnet Curie temperature (Tc) which means its magnetic field strength is increased at higher temperatures
- Heavy rare earth elements such as dysprosium or terbium are substituted to neodymium to improve the coercivity at higher temperatures
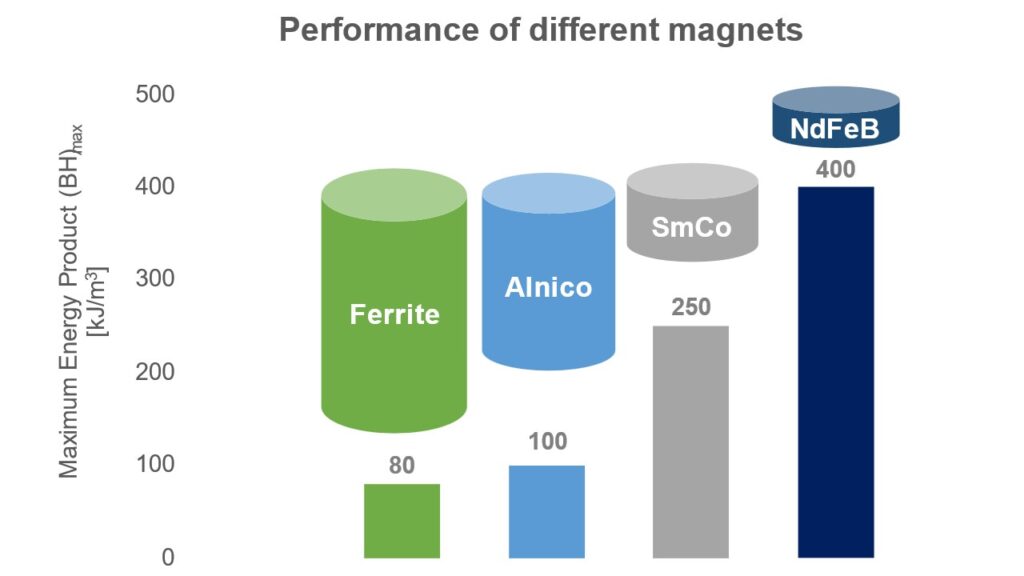
- NdFeB magnets have the highest energy density which allows the use of smaller magnets – miniaturization
- About 50 % of current magnet sales (in $ value) are NdFeB magnets
- Due to their strength, they are essential in many applications in everyday life (electronics, health care, energy efficient appliances) and to build a more sustainable future (EV, clean energy)
- The forecasted increase of demand for NdFeB magnets is driven by the growth of clean energy sector and electric vehicles
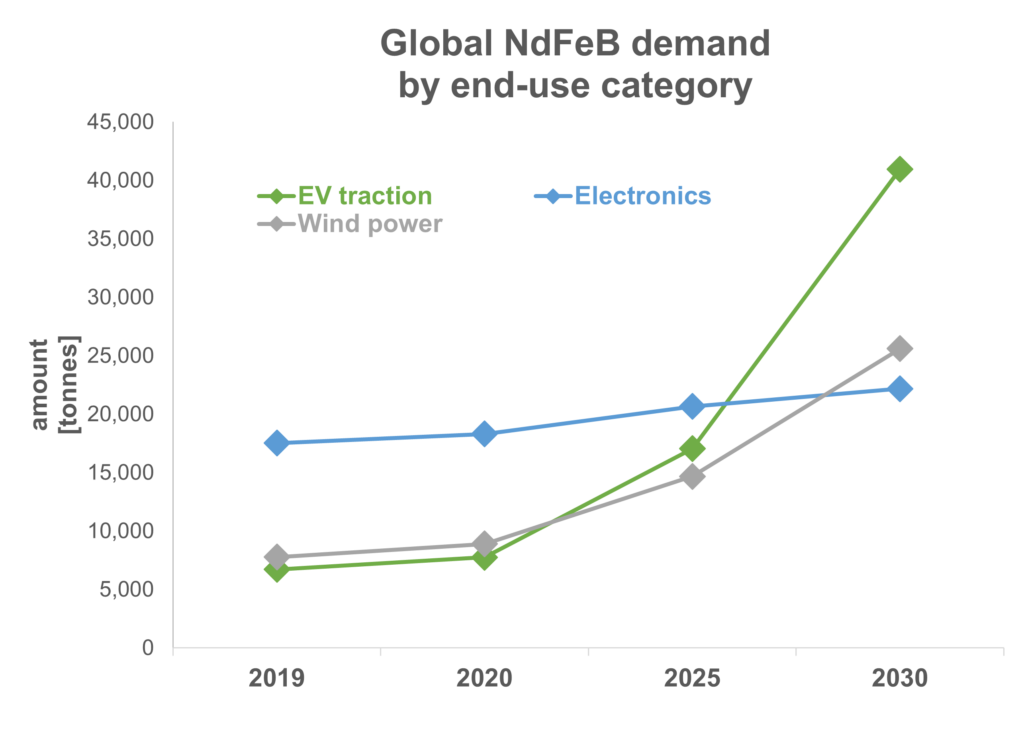
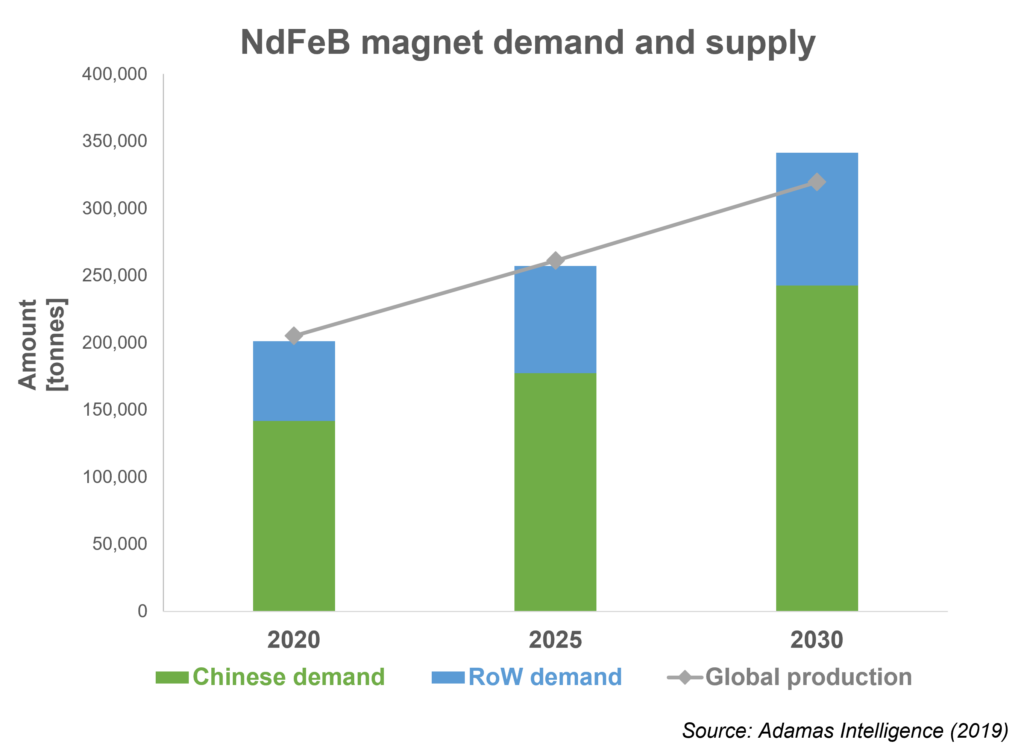
- The current global market for NdFeB is about 200,000 tons
- The global demand is expected to increase by 70 % in 2030
- About 90 % of the global production is dominated by China
- In 2030, about 84 % of China’s production would be used for domestic consumption which could lead to shortages in supply